Cortisone
Cortisone is a steroid produced in the adrenal glands of the human body. The isolation of cortisone from the mixture of molecules produced in these glands was carried out by American biochemist Edward Kendall and coworkers. Kendall shared the Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine for this work in which he also helped establish the usefulness of cortisone in the treatment of arthritis.
The isolation of cortisone from adrenal glands is a laborious process, so its widespread utility as a medicine awaited the development of synthetic pathways to its production. Percy Julian was the first scientist to accomplish a commercially viable synthesis using protein from soybeans, and since his work an increasing number of applications have been found.
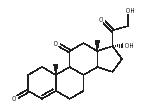
The structure of cortisone is shown above. Like other steroids, the molecule contains four fused rings. It is an example of an anti-inflammatory compound—one that reduces swelling. In many cases, swelling causes pain so the ability to reduce inflammation can be important for pain management, including the case of arthritis. In addition to arthritis, cortisone can be used to treat asthma, dermatological diseases, and tuberculosis and to fight the rejection of organ transplants by the body's immune system.
EDWARD KENDALL (1886–1972)
Edward Kendall recognized that symptoms of one type of arthritis decrease in females during pregnancy. He worked to isolate and identify hormones that could be responsible for this occurrence. It was during this search that cortisone was discovered in adrenyl glands. For this scientific breakthrough, Kendall was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1950.
—Valerie Borek
SEE ALSO Julian, Percy ; Steroids .
Thomas A. Holme
Bibliography
Crappo, L. (1985). Hormones. New York: W. H. Freeman.
Tonegawa, S. (1985). "The Molecules of the Immune System." Scientific American 253:122–131.