RHENIUM

Overview
Rhenium was discovered by a German research team that included Walter Noddack (1893-1960), Ida Tacke (1896-1979) and Otto Berg. These scientists knew that there were two empty boxes in the periodic table that represented elements that had not yet been discovered. The periodic table is a chart that shows how chemical elements are related to one another. In 1925, the German team announced that they had found both elements. They were correct about one (element number 75) but wrong about the other (element number 43).
Rhenium is one of the rarest elements in the world. At one time it sold for about $10,000,000 a kilogram (about $5,000,000 a pound). It is no longer that expensive, although it is still very costly.
Rhenium has some unusual properties. For example, it is one of the most dense elements known. It also has one of the highest boiling points of all elements.
SYMBOL
Re
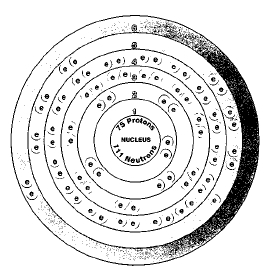
ATOMIC NUMBER
75
ATOMIC MASS
186.207
FAMILY
Group 7 (VIIB)
Transition metal
PRONUNCIATION
REE-nee-um
The primary uses of rhenium are in alloys that are used at very high temperatures or exposed to a great deal of wear.
Discovery and naming
At the beginning of the 1920s, chemists knew they were approaching a milestone. They had already isolated 87 chemical elements. But they knew that five more were waiting to be discovered. How did they know? Every element has a space in the periodic table. An empty space meant that an element was missing. In 1920, five empty spaces were still left in the periodic table.
Chemists worldwide were searching for these five elements. In 1925, Noddack, Tacke, and Berg reported that they had found two of those elements: numbers 43 and 75. They called the first element masurium, after the region called Masurenland in eastern Germany. They named element number 75 rhenium, after the Rhineland, in western Germany. Rhenium was the last naturally occurring element to be discovered.
When a discovery like this is announced, other chemists try to repeat the experiments. They see if they get the same results as those reported. In this case, the German team turned out to be half right. Scientists were able to confirm the existence of element 75. They were not able to confirm the Germans' discovery of element 43. In fact, it was another decade before element 43 (technetium) was actually discovered.
Physical properties
Rhenium is a ductile, malleable, silvery metal. Ductile means capable of being drawn into thin wires. Malleable means capable of being hammered into thin sheets. It has a density of 21.02 grams per cubic centimeter, a melting point of 3,180°C (5,760°F), and a boiling point of 5,630°C (10,170°F). These numbers are among the highest to be found for any of the chemical elements.
Rhenium is quite dense, which is unusual for a metal. When heated, most metals reach a point where they change from being ductile to being brittle. They can be worked with below that point, but not above it. Above this transition temperature they become brittle. If one tries to bend or shape them, they break apart. The unusual behavior of rhenium means that it can be heated and recycled many times without breaking apart.
Chemical properties
Rhenium is a moderately stable metal. It does not react with oxygen and some acids very readily. But it does react with strong acids such as nitric acid (HNO 3 ) and sulfuric acid (H 2 SO 4 ).
Occurrence in nature
About a third of all rhenium used in the United States comes from copper and molybdenum ores in the Western states. It is obtained during the process of copper mining. Two-thirds are imported from other countries, primarily Chile, Germany, and the United Kingdom. The principal ores of rhenium are molybdenite, gadolinite, and columbite.
Rhenium is one of the rarest elements in the world. Its abundance is thought to be about one part per billion.
Isotopes
Two isotopes of rhenium occur in nature, rhenium-185 and rhenium-187. Isotopes are two or more forms of an element. Isotopes differ from each other according to their mass number. The number written to the right of the element's name is the mass number. The mass number represents the number of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus of an atom of the element. The number of protons determines the element, but the number of neutrons in the atom of any one element can vary. Each variation is an isotope.
Rhenium-187 is radioactive. A radioactive isotope is one that breaks apart and gives off some form of radiation. The half life of rhenium-187 is about 100,000,000 years. The half life of a radioactive element is the time it takes for half of a sample of the element to break down. For example, of a 100-gram sample of rhenium-187, only half that amount, or 50 grams, would be left after 100,000,000 years. The other 50 grams would have broken down and changed into another isotope.
Rhenium was the last naturally occurring element to be discovered.
Extraction
Ores containing rhenium are first roasted, or heated in air, to convert
them to rhenium oxide (ReO
3
).
Hydrogen
gas is then passed over the rhenium oxide. The hydrogen converts the
rhenium oxide to the pure metal:








Uses
About three-quarters of all rhenium consumed in the United States are used in the manufacture of superalloys. A superalloy is an alloy made of iron, cobalt, or nickel. It has special properties, such as the ability to withstand high temperatures and attack by oxygen. Superalloys are widely used in making jet engine parts and gas turbine engines.
Alloys containing rhenium also have many other applications. They are used in making devices that control temperatures (like the thermostat in your home), heating elements (like those on an electric stove), vacuum tubes (like those in a television set), electromagnets, electrical contacts, metallic coatings, and thermocouples. A thermocouple is used like a thermometer for measuring very high temperatures.
About a quarter of the rhenium consumed in the United States is used as a catalyst in the petroleum industry. A catalyst is a substance used to speed up or slow down a chemical reaction without undergoing any change itself. Rhenium catalysts are used in the reactions by which natural petroleum is broken down into more useful fragments, such as gasoline, heating oil, and diesel oil.
Compounds
Very few compounds of rhenium have any commercial applications.
Superalloys are widely used in making jet engine parts and gas turbine engines.
Health effects
Complete studies on the health effects of rhenium are not available. For that reason, it should be assumed to be toxic and be handled with caution.