PALLADIUM

Overview
Palladium is found in Row 5, Group 10 (VIIIB) of the periodic table. The periodic table is a chart that shows how chemical elements are related to each other. Palladium, ruthenium, rhodium, osmium, indium, and platinum make up the platinum group of metals. These metals are also sometimes called the noble metals. That term reflects the fact that the six elements are not very reactive.
Palladium was discovered along with rhodium in 1803 by English chemist William Hyde Wollaston (1766-1828). Wollaston had been studying platinum ores, probably taken from South America.
Like the other platinum metals, palladium is quite rare. It also has a beautiful shiny finish that does not tarnish easily. These properties make it desirable in making jewelry and art objects. These uses are its most important applications.
SYMBOL
Pd
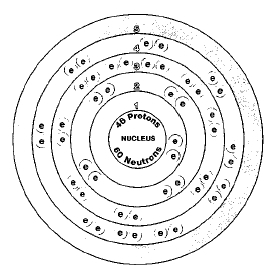
ATOMIC NUMBER
46
ATOMIC MASS
106.42
FAMILY
Group 10 (VIIIB)
Transition metal;
platinum group
PRONUNCIATION
puh-LAY-dee-um
Discovery and naming
As early as the 1700s, Brazilian miners described a number of platinum-like metals. They called them by such names as prata (silver), ouro podre (worthless or spoiled gold), and ouro bran-co white gold). These names may or may not have matched the materials that were actually present in the metals. For example, a substance the miners called platino (platinum) was probably a combination of gold and palladium.
In the early 1800s, Wollaston received samples of some of these metals. He decided to analyze them. During his work, he found that a sample of platinum ore contained other metals as well. These metals turned out to be two new elements—rhodium and palladium. The name palladium was taken from Pallas, an asteroid that had been discovered at about the same time.
Chemists later found palladium in other South American ores. A sample of ouro podre, for example, turned out to include about 86 percent gold, 10 percent palladium, and 4 percent silver.
Physical properties
Palladium is a soft, silver-white metal. It is both malleable and ductile. Malleable means capable of being hammered into thin sheets. Ductile means capable of being drawn into thin wires. The malleability of palladium is similar to that of gold. It can be hammered into sheets no more than about a millionth of a centimeter thick.
An interesting property of palladium is its ability to absorb (soak up) hydrogen gas like a sponge. When a surface is coated with finely divided palladium metal, the hydrogen gas passes into the space between palladium atoms. Palladium absorbs up to 900 times its own weight in hydrogen gas.
Chemical properties
Palladium has been called "the least noble" of the noble metals because it is the most reactive of the platinum group. It combines poorly with oxygen under normal conditions but will catch fire if ground into powder. Palladium does not react with most acids at room temperature but will do so when mixed with most hot acids. The metal will also combine with fluorine and chlorine when very hot.
Occurrence in nature
The abundance of palladium in the Earth's crust is estimated to be about 1 to 10 parts per trillion. That makes it one of the ten rarest elements found in the Earth's crust. It usually occurs
Russia and South Africa produce about 93 percent of the palladium mined in the world. It is also found in Canada and the United States.
Palladium combines poorly with oxygen under normal conditions but will catch fire if ground into powder.
Isotopes
There are six naturally occurring isotopes of palladium: palladium-102, palladium-105, palladium-106, palladium-108, and palladium-110. Isotopes are two or more forms of an element. Isotopes differ from each other according to their mass number. The number written to the right of the element's name is the mass number. The mass number represents the number of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus of an atom of the element. The number of protons determines the element, but the

About a dozen radioactive isotopes of palladium are known also. A radioactive isotope is one that breaks apart and gives off some form of radiation. Radioactive isotopes are produced when very small particles are fired at atoms. These particles stick in the atoms and make them radioactive.
No isotope of palladium has an important commercial use.
Extraction
Palladium is removed from platinum ores after platinum and gold have been removed. The metal is converted to palladium chloride (PdCl 2 ) and then purified as pure palladium.
Uses
Palladium has two primary uses: as a catalyst and in making jewelry and specialized alloys. A catalyst is a substance used to speed up or slow down a chemical reaction without undergoing any change itself. Palladium catalysts are used in breaking down petroleum to make high quality gasoline and other products. It is also used in the production of some essential chemicals, such as sulfuric acid (H 2 SO 4 ), which is used in paper and fabric production. The catalytic converters used in automobiles today may also contain a palladium catalyst. A catalytic converter is a device added to a car's exhaust system. It helps the fuel used in the car burn more efficiently.
An alloy is made by mixing two or more melted metals. The solid mixture has properties different from those of the individual metals. Palladium is commonly alloyed with gold, silver, and copper. The alloys are used in a variety of products, such as ball bearings, springs, balance wheels of watches, surgical instruments, electrical contacts, and astronomical mirrors. Palladium alloys are also used quite widely in dentistry.
Compounds
Relatively few palladium compounds are commercially important.
Many automobiles use a palladium catalyst to help fuel burn more efficiently.
Health effects
There is no evidence of serious health effects from exposure to palladium or its compounds.
& it showed how palladium was mined in
Canada; now I know what it is & used for ..
Thank you
Just a friendly correction! :)